96-82-2
- Product Name:Lactobionic Acid
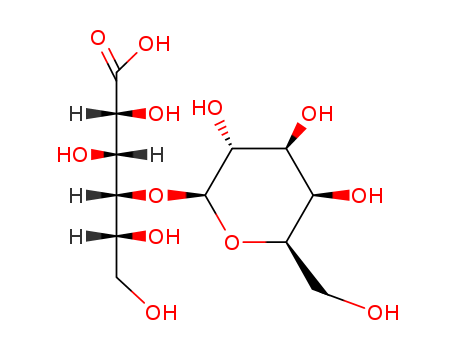
- Molecular Formula:C12H22O12
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:358.299
Product Details
pd_meltingpoint:113-118 °C(lit.)
Appearance:White to off-white crystalline powder
Top Quality Lactobionic Acid 96-82-2 Hot Sell In Stock
- Molecular Formula:C12H22O12
- Molecular Weight:358.299
- Appearance/Colour:White to off-white crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:7.15E-35mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:113-118 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:26 ° (C=8.8, H2O)
- Boiling Point:864.7 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:3.28±0.35(Predicted)
- Flash Point:319.1 °C
- PSA:217.60000
- Density:1.79 g/cm3
- LogP:-5.66890
Lactobionic acid(Cas 96-82-2) Usage
|
Properties |
Lactobionic acid has a molecular weight of 358.296 g/mol and a monoisotopic mass of 358.111 g/mol, which is also its exact mass. The compound has a heavy atom count of 24. Lactobionic acid has a melting point of 113-118°C and a boiling point of about 410.75°C. It is a white to off-white powder with a solubility of 10 g/100 mL in water and a density of about 1.4662. It is also slightly soluble in anhydrous methanol and ethanol. Lactobionic acid is hygroscopic, and it has a good water retention potential hence its applicability to cosmetic products. The compound and its constituent mineral salts (Ca, Na, and K lactobionate) are produced commercially for medical and industrial applications and in some cases for research purposes. |
|
Preparation |
The selective transformation of lactose into Lactobionic acid entails the oxidation of the radical aldehyde category of glucose on the lactose molecule to the carboxylic classification. The production of Lactobionic acid entails various processes which may include enzymatic synthesis, microbial production, biocatalytic oxidation, electrochemical oxidation and heterogeneous catalytic oxidation. |
|
Extraction and Purification |
To enhance the productive capacity of Lactobionic acid, the enzymatic reaction can be cut off after several hours of activity and the unchanged substrates can be re-injected into the cycle after the elimination of useful products. The effective process of separation is through liquid chromatography particularly because the recovered species are pure. Exposing the solution made of lactobionate ions through a sequence of ion-transfer resins produces a pure solution of Lactobionic acid with minimal amounts of calcium ions. Different techniques such as crystallization, evaporation, electrodialysis and ethanol precipitation can be employed to obtain Lactobionic acid. |
|
Physiological & Commercial Applications |
Lactobionic acid is an essential compound based on its chelating properties and its ability to form complex bonds with Ca, Fe, Cu, and Mn. Its incorporation into food additives can stimulate mineral absorption and Ca2+ in the intestines hence enhancing one’s health. Lactobionic acid is unaffected by digestive enzymes hence it is a valuable ingredient in the preparation of functional foods. It is poorly absorbed into the linings of the intestines hence it can also be a Bifidus booster molecule for functional beverages and foods. It enhances the healing process of wounds hence it is valuable in oral, skin, nail, hair and vaginal mucosa care. As an antioxidant, Lactobionic acid acts by suppressing the synthesis of hydroxyl radicals due to its iron chelating ability. As a food additive, Lactobionic acid functions as an acidifier in products containing fermented milk, an aging suppressor for bread, an antioxidant, and as a gelling or stabilizing medium in desserts. In cosmetics, Lactobionic acid is applied as an active ingredient in regenerative and antiaging skin-care products based on its therapeutic properties. Its metal chelation potential suppresses the degeneration potential of metalloproteinase enzymes, which decreases the appearance of aging wrinkles. In the chemical industry, Lactobionic acid is an active ingredient (sugar-based surfactant) in biodegradable detergents. It may also be used in drug delivery systems, nanoparticle diagnosis and tissue engineering. |
|
Biotechnological Production |
Currently, lactobionic acid is produced by chemical synthesis using refined lactose as feedstock. This process is expensive due to the energy demand. Alternatively, Acidic Organic Compounds in Beverage, Food, and Feed Production 111 enzymatic processes have been suggested. For example, lactose could be reacted to lactobionic acid using an enzymatic system with co-factor regeneration. First, lactose is converted to lactobionolactone by a cellobiose dehydrogenase. This reaction requires an electron acceptor, which is regenerated by a laccase reducing oxygen to water. Finally, lactobionolactone spontaneously hydrolyzes to lactobionic acid. Moreover, microbial production of lactobionic acid has been described. In a fed-batch cultivation of Burkolderia cepacia growing in a complex medium (lactose, salts, peptone, and yeast extract), a final titer of 400 g.L-1, a yield of approximately 1.0 g of lactobionic acid per gram of lactose, and a productivity of 1.67 g.L-1.h-1 have been achieved. Another promising strategy for an inexpensive biotechnological process is the utilization of cheap raw materials. For example, lactobionic acid could be obtained from concentrated cheese whey by fermentation with Pseudomonas taetrolens. In a fed-batch process, a product concentration of 164 g.L-1 with a productivity of 2.05 g.L-1.h-1 and a yield of 0.82 g of lactobionic acid per gram of lactose have been observed. Furthermore, whole-cell biocatalysis using permeabilized Zymonmonas mobilis cells and an equimolar mixture of lactose and fructose has been tested. In a batch process, a maximum lactobionic acid concentration of 268 g.L-1 and a conversion rate of 72 % within 24 h have been measured. The productivity of lactobionic acid was 11.2 g.L-1.h-1 . |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise lactobionic acid from water by addition of EtOH. [NMR: Taga et al. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 51 2278 1978, Beilstein 17 III/IV 3392, 17/7 V 436.] |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A disaccharide formed between beta-D-galactose and D-gluconic acid. |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H22O12/c13-1-3(15)10(7(18)8(19)11(21)22)24-12-9(20)6(17)5(16)4(2-14)23-12/h3-10,12-20H,1-2H2,(H,21,22)/t3-,4-,5+,6+,7-,8-,9-,10-,12+/m1/s1
96-82-2 Relevant articles
Aqueous oxidation of sugars into sugar acids using hydrotalcite-supported gold nanoparticle catalyst under atmospheric molecular oxygen
Tomar, Ravi,Sharma, Jatin,Nishimura, Shun,Ebitani, Kohki
supporting information, p. 843 - 845 (2016/07/16)
Hydrotalcite-supported gold nanoparticle...
Gold as active phase of BN-supported catalysts for lactose oxidation
Meyer, Nathalie,Renders, Coralie,Lanckman, Rapha?l,Devillers, Michel,Hermans, Sophie
, p. 549 - 558 (2015/01/30)
Au/h-BN catalysts have been prepared by ...
Boron nitride as an alternative support of Pd catalysts for the selective oxidation of lactose
Meyer, Nathalie,Bekaert, Kevin,Pirson, Damien,Devillers, Michel,Hermans, Sophie
, p. 170 - 174 (2013/01/15)
The potential of boron nitride as innova...
Selective production of lactobionic acid by aerobic oxidation of lactose over gold crystallites supported on mesoporous silica
Gutierrez, Luis-Felipe,Hamoudi, Safia,Belkacemi, Khaled
body text, p. 94 - 103 (2012/04/10)
Partial oxidation of lactose over Au-bas...
96-82-2 Process route
-
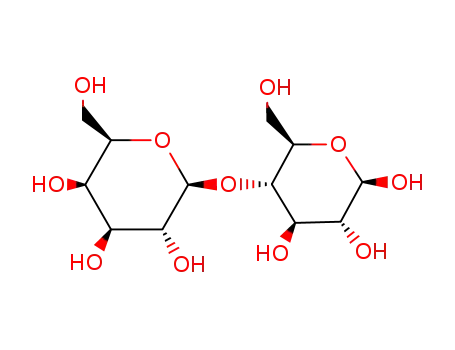
- 5965-66-2
LACTOSE

-
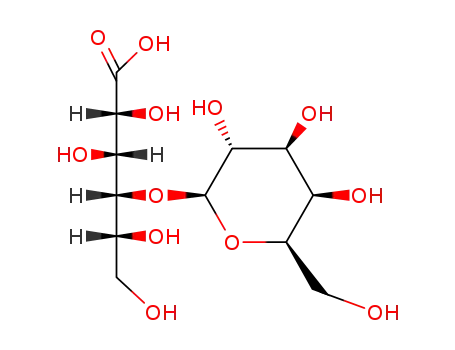
- 96-82-2,534-41-8,534-42-9,51267-45-9,58459-39-5,69728-97-8,21675-39-8
lactobionic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With oxygen; In water; at 39.84 ℃; for 3h; under 760.051 Torr; Schlenk technique;
|
96.1% |
|
With oxygen; potassium hydroxide; at 40 ℃; for 4h; pH=9; Reagent/catalyst;
|
64% |
|
With oxygen; Bi-promoted Pd on carbon; In water; at 150 - 170 ℃; for 5.5h; under 5331.76 - 5910.98 Torr; Conversion of starting material; Gas phase;
|
|
|
With oxygen; 5% alumina-supported platinum catalyst; at 80 ℃; under 750.075 Torr; pH=8; Product distribution / selectivity;
|
|
|
With oxygen; 5 % alumina-supported palladium; at 80 ℃; under 750.075 Torr; pH=8; Product distribution / selectivity;
|
|
|
With oxygen; 0.5% Au/TiO2; at 80 ℃; under 750.075 Torr; pH=8; Product distribution / selectivity;
|
-
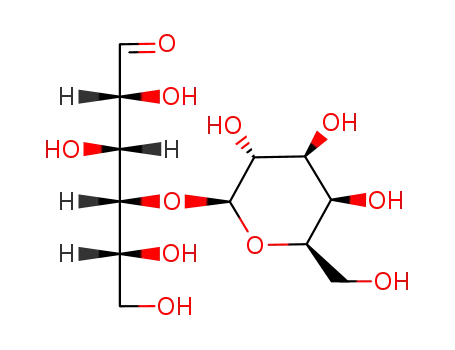
- 63-42-3
D-(+)-lactose

-

- 96-82-2,534-41-8,534-42-9,51267-45-9,58459-39-5,69728-97-8,21675-39-8
lactobionic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With oxygen; for 2h; Reagent/catalyst;
|
100% |
|
With sodium hydroxide; palladium dichloride; potassium hexacyanoferrate(III); In water; at 35 ℃; Rate constant; Thermodynamic data; Eact, ΔS(excit.), ΔH(excit.), ΔG(excit.);
|
|
|
With sodium hydroxide; potassium hexacyanoferrate(III); In water; at 35 ℃; Rate constant; Thermodynamic data; Eact, ΔS(excit.), ΔH(excit.), ΔG(excit.);
|
|
|
With calcium carbonate; calcium bromide; in wss. Loesung bei der elektrochem. Oxidation an Graphit-Anoden;
|
|
|
With water; bromine; barium benzoate;
|
|
|
With barium dihydroxide; barium(II) iodide; iodine; in wss. Loesung;
|
|
|
With sodium carbonate; sodium bromide; wss. Loesung, anschl. mit Chlor und Natriumcarbonat;
|
|
|
With calcium chlorite; water; calcium carbonate;
|
|
|
With bromine; calcium carbonate;
|
|
|
With potassium bromide;
|
|
|
mit Hilfe von Kulturen von Pseudomonas gluconium und Pseudomonas woodsii;
|
|
|
mit Hilfe von Kulturen von Bacterium anitratum;
|
|
|
With water; bromine; sodium hydrogencarbonate;
|
|
|
mit Hilfe von Kulturen von Pseudomonas graveolens;
|
|
|
With Au on mesoporous silica nanoparticles; at 65 ℃; pH=9; aq. buffer;
|
|
|
With calcium hydroxide; water; iodine; anschl. mit Chlor und Calciumhydroxid;
|
|
|
With calcium hydroxide; calcium bromide;
|
|
|
With bromine; calcium carbonate;
|
96-82-2 Upstream products
-
6057-48-3
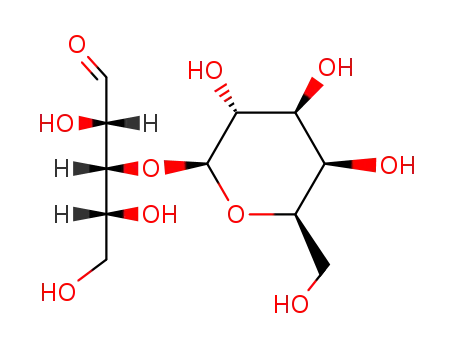
3-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-arabinose
-
63-42-3

D-(+)-lactose
-
5965-65-1
lactobionolactone
-
5965-66-2

LACTOSE
96-82-2 Downstream products
-
5965-65-1

lactobionolactone
-
888616-12-4
N-[1-(dodecylcarbamoyl-2-(trityl)imidazolyl)ethyl]-22-lactobionamido-12,12,13,13,14,14,15,15,16,16,17,17,18,18,19,19-hexadecafluorodocosanamide
-
918802-82-1
N-galactosylamino-N'-phenylpiperazine
-
173543-54-9
lactoseamidemethylbenzoic acid
Relevant Products
-
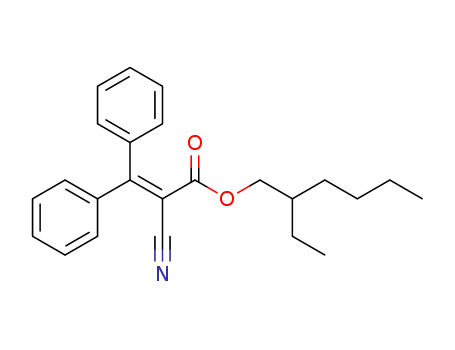
0ctocrylene
CAS:6197-30-4
-
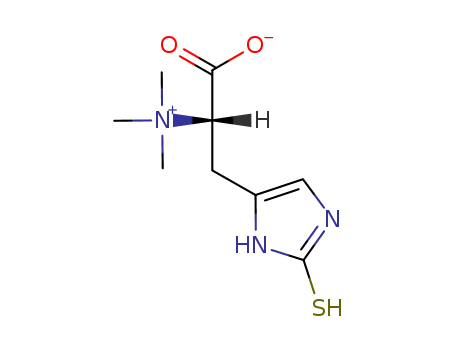
Ergothioneine
CAS:497-30-3
-
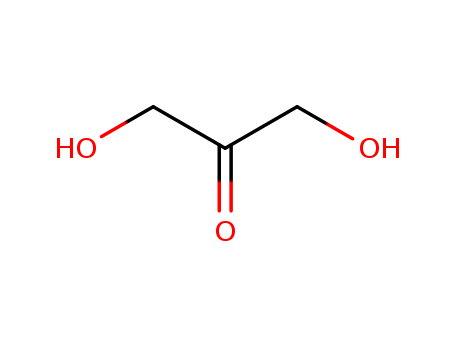
1.3-Dihydroxyacetone
CAS:96-26-4